Insomnia can often be prevented by making simple lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits and following a regular schedule.
Read more about Good Sleep Practices:
13 Steps To Better Quality Sleep
Importance of Sleep
Latest Stories
- Although the exact cause of lupus and other autoimmune diseases is unknown, most believe that lupus results from both genetic and environmental stimuli. Since lupus is known to occur within families, doctors believe that it is possible to inherit a genetic predisposition to lupus. It is probable that having an inherited predisposition for lupus makes the disease more likely only after coming into contact with some environmental trigger. The higher number of lupus cases in females than in males…
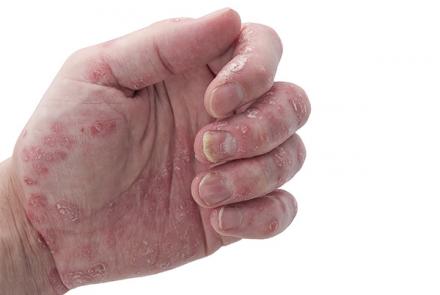
- Each person with lupus has slightly different symptoms that can range from mild to severe and may come and go over time. Usually the joint and muscle pain, rashes on skin are seen all the time but the intensity of the symptoms decrease with treatment. Painful or swollen joints and muscle pain Unexplained fever Red rashes, most commonly on the face Chest pain upon deep breathing Unusual loss of hair Pale or purple fingers or toes from cold or stress (Raynaud's phenomenon) Sensitivity to the sun…
- There are several types of lupus: 1. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the form of the disease that most people are referring to when they say “lupus”. The word “systemic” means the disease can affect many parts of the body. Although SLE usually first affects people between the ages of 15 and 45 years, it can occur in childhood or later in life as well. 2. Discoid lupus erythematosus is a chronic skin disorder in which a red, raised rash appears on the face, scalp, or elsewhere. The…
- As signs and symptoms vary considerably from person to person, there is no single diagnostic test that can confirm lupus. In addition, signs and symptoms tend to change over time and are similar to those of other disorders and diseases. These fluctuations in disease activity make lupus extremely challenging to diagnose. The doctor may suggest some of the following: Complete blood count (CBC) to detect anaemia, low platelet count, and low white blood cell count. Antibody tests that includes…
- There is no cure for lupus. However, treatment options to control symptoms are available. Most people with lupus can lead active, healthy lives. Treatment plans should meet the individual patient's needs and may change over time. To develop a treatment plan, the doctor tries to: Prevent flares Treat flares when they do occur Minimise complications Mild forms of the disease may be treated with: NSAIDs for joint symptoms, after talking with your doctor Corticosteroid creams for…
- What you can do to cope up with the disease It is vital that you take an active role in your treatment. One key to living with lupus is to know about the disease and its impact. Being able to spot the warning signs of a flare-up can help you prevent the flare or make the symptoms less severe. Many people with lupus have certain symptoms just before a flare, such as: Feeling more tired Pain Rash Fever Stomach ache Headache Dizziness You should see your doctor often, even when symptoms are not…
- There is no known way to prevent Lupus since there is no known cause as yet. You can help manage flare-ups though: Avoid known triggers such as sunlight, stress, and lack of sleep Manage your diet Get adequate exercise
- Can migraines be prevented If you know what triggers your migraine, you can avoid it. Alternately, your doctor may prescribe preventive medications like beta blockers (propranalol, timadol, metoprolol, nadolol, atenolol), calcium channel blockers (nefidipine, diltiazem, verapamil). These drugs reduce the attack frequency in migraine patients. Other preventive medication are serotonin antagonists like methysergide, tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, doxepin).