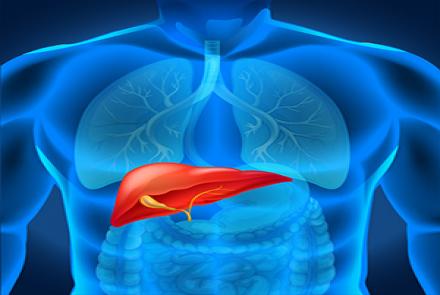
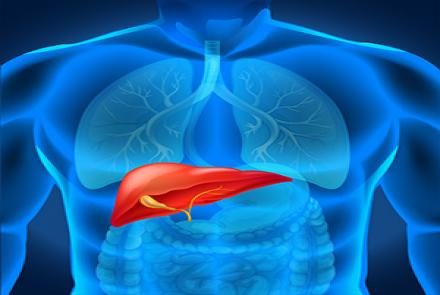
Chronic hepatitis is suspected when one has typical symptoms or signs and shows abnormally high liver enzymes on routine blood tests (which may be done for other reasons too). Blood tests are usually performed to determine proper function of the liver. Such tests and physical examination help establish or exclude the diagnosis, identify the cause, and also determine the severity of liver damage. Blood tests especially serological detection of Hepatitis antigens may then be done to identify…
Latest Stories
- Injectable interferon alpha was the first therapy approved for chronic hepatitis B. Lamivudine was the first approved oral nucleoside analogue for viral hepatitis. For drug induced hepatitis, the etiological drug is withdrawn and usage is stopped immediately. In case of alcoholic hepatitis, first-line treatment is discontinuation of alcohol.
- There are really no types of chronic hepatitis. There are only strains of A, B and C
- Lifestyle Recommendations: Living with Chronic hepatitis may not affect daily activities but a high-calorie diet is recommended. Many people develop nausea and may not be able to take food later in the day, so the bulk of intake is concentrated in the earlier hours of the day. In the acute phase of the disease, intravenous feeding may be needed if patients cannot tolerate food and have poor oral intake subsequent to nausea and vomiting. Avoid taking drugs that are metabolized by the liver…
- In order to prevent hepatitis the Center for Disease Control recommends routine vaccination of all children under the age of 19 with the hepatitis B, which starts at birth and another 2 doses which can be given within 18 months of birth date. Adults can also take Hepatitis A and B vaccines if eligible or if they are at high risk.
- Epilepsy can be treated. 1) Medication Generally doctors begin the treatment for epilepsy with medication. If the patient is not responding to medications, doctors may advise surgery. Many drugs are available to treat epilepsy and the choice of drug is based on the factors specific to patient. Medications used to treat epilepsy include: Carbamazepine (Tegretol or Carbatrol) Diazepam (Valium) Eslicarbazepine (Aptiom) Felbamate (Felbatol) Ethosuximide (Zarontin) Lacosamide (Vimpat)…
- A doctor may sometimes indicate a type of epilepsy based on whether the cause is known and identified (symptomatic) or cause is known but not identified (cryptogenic) or cause is not known (idiopathic). The types of seizures are also important in the treatment approach. What are the types of seizures? 1) Focal (partial) seizures They are produced by a relatively small part of the brain. They are of two types Simple partial seizures : characterized by…
- How is Epilepsy Diagnosed? Medical History A complete physical examination. Neurological examination Complete neurological examination to rule out behavioral modifications, change in mental function, motor abilities etc. Laboratory tests for Epilepsy Blood tests : Blood sample will be collected to check for signs of infection, genetic conditions etc. Electroencephalogram (EEG) : Routinely used diagnostic test which measures electrical impulses in the brain. This…
- What are the signs and symptoms of Epilepsy? Temporary confusion Uncontrollable jerking movements of arms and legs (commonly referred to as seizures) Loss of consciousness Staring spell What are the complications of Epilepsy? Falling: which causes injury to your head or break a bone Drowning : if you have epilepsy you are 15 to 19 times more likely to drown while swimming or bathing than rest of the population Accidents : A seizure that causes either loss of awareness or control can be…