Persons with diabetes often get extremely stressed when their doctor wants to move them from pills to insulin shots. Dr Shital Patel allays the fears and explains what to expect and how to go about it.
The transition from pills to insulin injections can be a worrying experience for many Diabetes Type 2 patients. You should know that this does not mean that your diabetes has worsened or that your Type 2 diabetes has changed to Type 1. You are being prescribed insulin because after 6-10 years of diabetes treatment, often the body is unable to control the blood sugar levels on pills alone and needs insulin to keep diabetes in control.
Diabetes pills can only work as long as the body produces some of its own insulin. If your blood glucose levels remain high after meals and if your A1C is not optimum (even though you are taking oral diabetes medication), your doctor may wish to start you on insulin. Your doctor may prescribe you a pill-insulin combination or switch to insulin only therapy depending on your blood tests.
Initially it may take a bit of getting used to but it’s a change that can really help you have better control of your diabetes. And remember, there is always support and help if you need it from your doctor or a nurse.
Here are a few tips on what to expect:
Facing the change
Many people will tell you that an insulin shot is less painful than pricking your finger during a blood glucose check. But the first shot on your own is never easy. While some people want a family member around for support, other may prefer to be alone. Give yourself time to prepare mentally and take deep breaths to calm yourself. It really doesn’t hurt.
Lifestyle adjustments
When you’re on insulin, you need to be aware of your blood glucose level and insulin need. This means:
• Eating your meals on time
• Coordinating your insulin dose with your meals and the amount of physical activity you have done. Initially your doctor will prescribe a set timed dose, but once you are more confident and understand how it works, you can adjust according to meals timings and physical activity.
• Close monitoring of your blood glucose level – your doctor will advise frequency
All this may sound inconvenient but it is a matter of habit and it will keep your blood sugar better regulated. Luckily, several new kinds of insulin are now available that allow you to do everything that you’ve always done, for instance, exercise, dine out, travel and even skip a meal or two.
Types of Insulin
There are different types of insulin depending on how quickly they work, when they peak, and how long they last. Insulin is available in different strengths; the most common is U-100.
Rapid-acting insulin: This starts working instantly, peaks in an hour and lasts for a couple of hours. Eg: Insulin glulisine (Apidra), insulin lispro (Humalog), and insulin aspart (NovoLog).
Regular- or short-acting insulin: This kicks in about 30 minutes, peaks at 2-3 hours and lasts for 3-6 hours. Eg: Humulin R, Novolin R.
Intermediate-acting insulin: This takes 2 to 4 hours to work fully, peak at 4-12 hours and its effects last up to 18 hours. Eg: NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N).
Long-acting insulin: There are no peak levels, and it can keep working for an entire day. Eg: Insulin detemir (Levemir) and insulin glargine (Lantus).
It's possible that you may need more than one type of insulin or to take it more than once a day. Depending upon your specific needs, your doctor may wish to prescribe other medications along with insulin.
How & when to take insulin
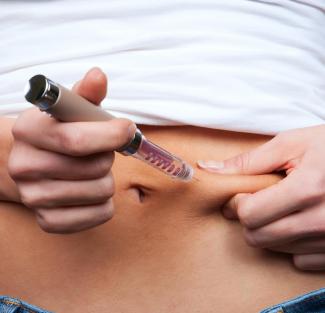
• Insulin injections are administered using either a syringe or an injection pen, which is also called an insulin pen (auto-injector). Most people need between 2-4 injections a day.
• Insulin is taken before meals. The time will vary depending on the type of insulin. It’s important to keep to a daily regimen for taking insulin. Discuss the different options with your doctor, such as a long-acting and rapid-acting insulin plan, using an insulin pen or switching to an insulin pump, to find one that works with your condition and lifestyle. (An Insulin pump is a cannulae put under the skin that just needs the press of a button for insulin delivery and can be programmed as per your needs. The injection or pen is less complicated to use.)
• Eating at fixed times everyday also makes it easier to manage your blood glucose.
• Keep insulin ready before meals to prevent hyperglycaemia. It’s easier to keep blood glucose from going too high by having insulin in your body when you eat than to lower it later. Give your insulin a head-start!
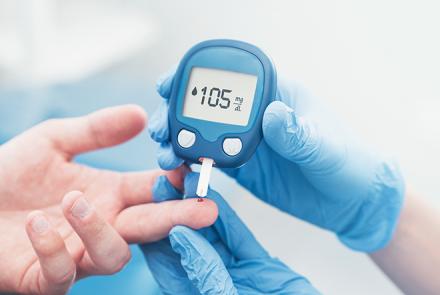
Blood glucose monitoring
Self-monitoring becomes an essential part of the transition to insulin to better regulate your insulin intake. This requires using a glucometer at home. This is a small handheld device to check blood glucose. Your doctor or nurse can provide you with the training on how to use one. Continuous glucose monitoring device (attached to the body) is also available for patients who require a more timely supervision. The HbA1c test is a blood test used to measure blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months. Your doctor may prescribe this from time to time.
Insulin side-effects
The insulin that you inject is practically identical to the insulin that your body makes. Insulin is a hormone, so it’s safe and natural. The major side effect of insulin is low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) and that can easily be prevented and treated.
Hypoglycaemia usually happens if the patient does not eat on time or takes too much insulin. It’s easily avoided by keeping to a fixed meal and injection time. The best way to treat mild to moderate hypoglycemia is by eating sugar. For more severe cases, patient must be given a glucagon injection. Other side-effects include initial weight gain, scarring or rash at site of frequent injections. With inhaled insulin, there's a risk of a sudden tightening of the lungs in people who have asthma or COPD. Diabetes pills, while extremely beneficial, have more side effects than insulin.
Sticking to your insulin plan
Insulin is a big step for most people with Type 2 diabetes. Some patients struggle to keep up with it and often skip an injection if they think they’re okay for the day. Also, people who get insulin allergic reactions or gain weight have less compliance than others. Discussing all these issues with your doctor or diabetes educator will open up more options regarding treatment and coping with it.