Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can occur in any part of the urinary tract. Most UTIs are caused by bacteria. They can also be caused by fungi or viruses.
UTIs are the second most common type of infection in humans. The National Kidney & Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NKUDIC) reports that UTIs account for over eight million doctor visits annually.
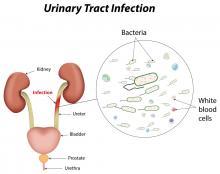
Anything that reduces the bladder emptying or irritates the urinary tract can cause UTIs. Many factors can put someone at risk.
- Obstructions: Blockages that make it difficult to empty the bladder can cause an UTI. Obstructions can be caused by an enlarged prostate, kidney stones and certain forms of cancer.
- Gender: Women are more likely to get UTIs. This is because their urethras are shorter. UTIs in men are less common and more serious.
- Sexual Activity: Pressure on the urinary tract during sex can move bacteria into the bladder. Most women have bacteria in their urine after intercourse. However, the body usually can get rid of these pathogens within 24 hours.
- Bathroom Hygiene: Wiping from back to front after going to the bathroom can lead to a UTI. This motion drags bacteria from the rectal area towards the urethra.
- Spermicides (Contraceptives – substance that kills the spermatozoa): Spermicides can increase UTI risk. They may cause skin irritation in some women. This increases the risk of bacteria entering into the bladder.
- Condoms: Latex condoms can cause increased friction during intercourse. They may also irritate the skin. This may increase the risk of UTI in some individuals. However, condoms are important for reducing the spread of sexually transmitted infections.
- Diaphragms: Diaphragms may put pressure on the urethra. This can decrease bladder emptying. Some studies have seen a higher UTI risk in women who use diaphragms.
- Diabetes: Diabetes may make patients more susceptible to UTI due to impaired host defense mechanism.
- Loss of Oestrogen (Hormone): After menopause, a loss of oestrogen changes the normal bacteria in the vagina. This can increase the risk of UTI.
- Prolonged Use of Bladder Catheters: Catheters are used when someone cannot urinate normally. These thin, flexible tubes are inserted into the bladder. They allow urine to drain into a container. Long-term catheter use can increase the risk of UTI. They may make it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder. Treatment for a catheter-associated UTI may require removal of the device.
Changed
11/Nov/2015
Condition













