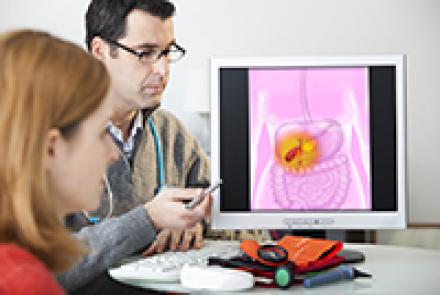
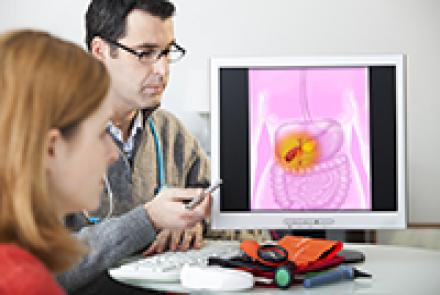
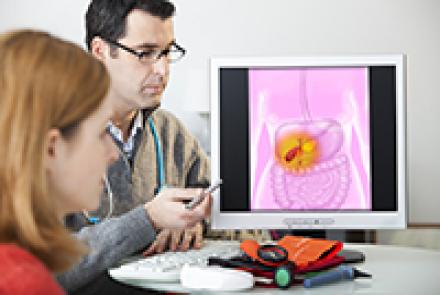
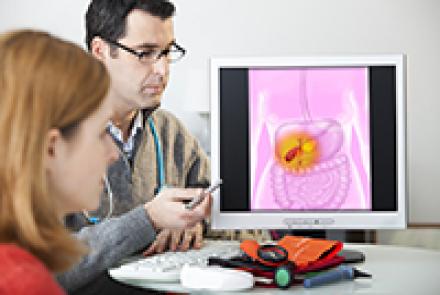
Ovarian cancer is cancer that develops in one or both the ovaries. It can then spread to other parts of the body.
The annual incidence of ovarian cancer globally is 204,000. It has a high fatality rate as more than 70% are diagnosed at an advanced stage.
We do not yet know what causes Ovarian Cancer. But we do what increases the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
You are at higher risk of developing ovarian cancer if:
- You are over 55; the average age at diagnosis is found to be 63
- You have a family history (risk is higher for 1st degree relatives)
- You have BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation
- You have a history of breast, uterine or colorectal cancer
- You have a genetic link to Lynch syndrome
- You started menstruating before 12 yrs of age
- You have never given birth or had children after 30
- You have been on estrogen based fertility medication
- You have had hormone therapy after menopause
- You have infertiltiy issues or endometriosis
- You smoke
- You are overweight
- You are from an Eastern european or Ashkenazi jewish descent.
Changed
23/Jan/2019
Community
Condition