Ovarian cancer is cancer that develops in one or both the ovaries. It can then spread to other parts of the body.
The annual incidence of ovarian cancer globally is 204,000. It has a high fatality rate as more than 70% are diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer usually involves chemotherapy and surgery, and sometimes radiotherapy.
- Surgery is the the first recommended option during the initial stage when the size of the tumour is small. The surgery may include removal of one (unilateral oophorectomy) or both ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy), the fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and the uterus (hysterectomy). If the cancer has spread to other organ such as the digestive tract, bladder, spleen etc, removal of those parts may be necessary, making it a more complex surgery. If the cancer is too wide-spread neoadjuvant chemotherapy will be given to shrink the tumours before surgery. Your Gynaecological Oncologist will also discuss all complications including fertility before the surgery. Side effects of surgery for ovarian cancer includes short-term pain and tenderness in the area of the operation. Wound care and prevention of any infection is important. Patients should discuss pain relief options with their doctor. Patients will also be put on blood thinners and compression stockings to avoid risk of clots. Average stay in the hospital may be a week.
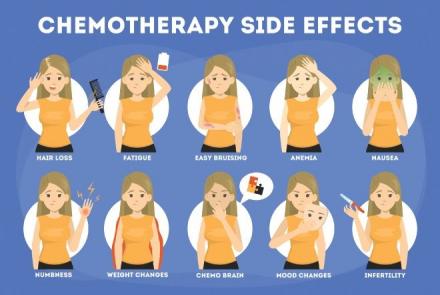
- Chemotherapy is the use of drugs, intravenous or oral, to treat cancer and can be used alone or adjunct/combination with surgery. Chemotherpay would start 2-4 weeks after surgery is done. If the tumour is less than 1cm after surgical debulking, intraperitoneal chemotherapy can be an option, where the chemo drug is given directly into the abdominal cavity through a tube.Side effects include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, mouth sores, loss of appetite, hair loss, sexual dysfunction, swollen hands and feet, change in bowel habits, anxiety and depression.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to destroy cancer cells. It is not effective for advanced stages because when vital organs are in the radiation field, a high dose cannot be safely delivered. Side effects include loss of taste sensation, mucositis, tiredness, flu-like symptoms, hair loss, osteoradionecrosis (necrosis and death of the bone due to radiation). Intraperitoneal radiation therapy for ovarian cancer may cause abdominal pain and bowel obstruction (a blockage of the intestine).
- Targeted therapy is the use of specific drugs that block cancer cells from growing. For advanced epithelial tumours, Bevacimab is given alongside chemotherapy. In patients with BRCA mutations, Olaparib is used in tablet form. Side effects are fewer than chemotherapy as it does not target healthy cells. Side effects can include nause, vomiting, abnormal blood cell counts etc.
- Palliative care works to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. It could be administered alongside other treatments and is meant to make the patient as comfortable as possible. It may include chemo and radiation therapy to slow the spread of the cancer. It also takes into account psychological, social and spiritual aspects of care.
Changed
24/Jan/2019
Community
Condition