Dyskinesia is a term that is used to describe excessive movement which is beyond one’s control.
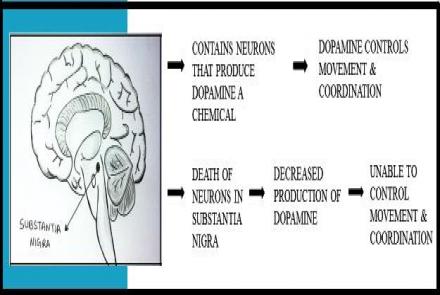
Scientists believe that the areas in the brain which are responsible for producing movement become over – stimulated. This leads to excessive and unwanted movement.
However, remember that dyskinetic movements are not tremors. Tremor is a symptom of Parkinson’s, whereas dyskinesia is more often thought to be a side effect of Levodopa.
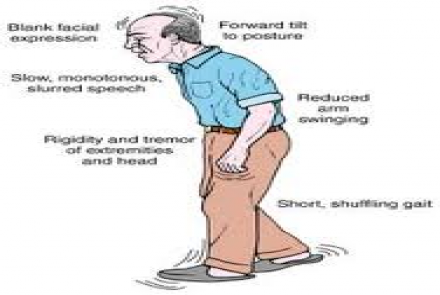
People experience different kinds of dyskinetic movements. These movements may be in the form of twitching, jerking, twisting movements or even restlessness. These movements are generally fast and are often painless & it can affect different parts of the body for different people.
For some, the dyskinesias may interfere with their day to day activities and for others; it may be so mild that it may go unnoticed.
What is the cause?
The exact cause is still unknown; however scientists believe that it may be associated with long term treatment with Parkinson’s medications particularly levodopa. As Parkinson’s progresses, the ability of the brain to produce dopamine further decreases. With time, the brain becomes more sensitive and hence starts responding to smaller amounts of dopamine. A combination of an increased sensitivity to levodopa and the natural progression of Parkinson’s are thought have been implicated for causing dyskinetic movements.
Hence levodopa treatment for individuals with young onset Parkinson’s is commenced during the later stages of the condition so as to avoid or delay the onset of dyskinesia.
Coping with dyskinesia
If you feel you may be having these movements, it’s advisable to consult your neurologist. Your doctor would then alter your medications and the dosage and help you achieve a balance between your symptoms and dyskinesias.
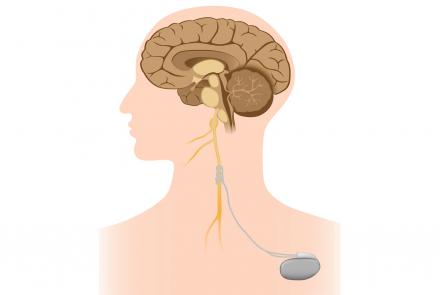
If medication doesn’t help, and if the dyskinesia is affecting you to a large extent, your doctor may recommend you to consider surgical options i.e. deep brain stimulation.
It is important to note that dyskinesias are a rare occurrence, and does not affect everyone. Each person with Parkinson’s is dissimilar, and will react differently to medications. Not everyone with Parkinson’s will have dyskinesias.”