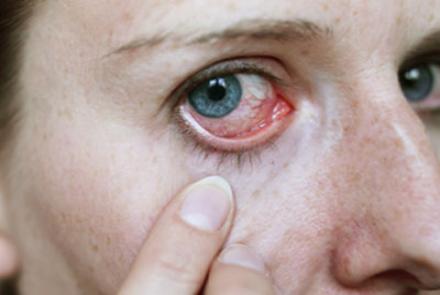
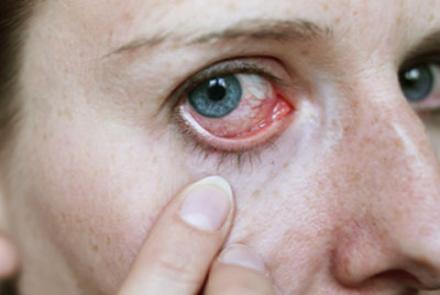
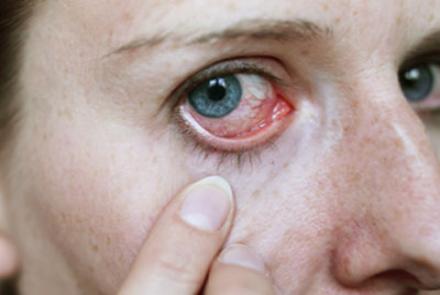
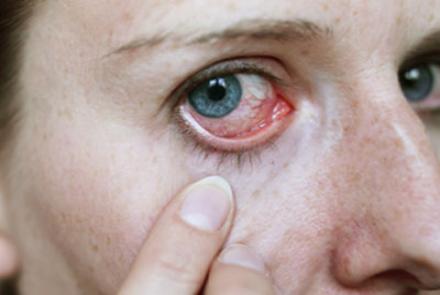
Dry eye disease is a growing public health problem and one of the most common conditions seen by eye practitioners. It is an extremely common and often unrecognised disease affecting millions of people. It is a multifactorial disease of the tears and ocular surface that results in symptoms of discomfort, visual disturbance and tear film instability with potential damage to ocular surface.
Treatment modalities:
The treatment of dry eyes can be divided into:
- Medical therapy: Is the mainstay of treatment for mild to moderate type of dry eyes. Tear substitutes or artificial tears are aqueous solutions containing polymers that determine their viscosity, retention time and adhesion to ocular surface. In moderate to severe cases, where there is a lot of inflammation, drugs like topical cyclosporine A and corticosteroids are administered. Oral tetracycline and essential fatty acids like omega 3 and omega 6 have also proven useful in interrupting the inflammatory cascade of dry eye diseases.
- Supportive therapy: This forms a very important mode of treatment to prevent worsening of dry eyes disease. Anyone who uses screens for long duration of time is advised to follow the rule of 20-20, i.e. is a break of 20 seconds from screen after every 20 minutes use of screen time. This allows the person to blink normally. The PC monitors should be slightly below the eye level. Contact lens users should use artificial tears which are preservative free to prevent dryness. Excessive pollution also contributes to dryness, hence glasses or glares should be used by everyone working outdoors.
- Treatment of underlying cause: Conditions like chronic blepharitis and refractive errors should be treated.
- Surgical therapy: Temporary occlusion of the punctum is done to block the drainage of tears. Thus retention time of the artificial as well as natural tears is prolonged in the eye, For severe cases, permanent occlusion or lid taping is done.
Surgical treatment
In patients who continue to have significant pathology despite medical therapy, surgical treatment may be considered in a stepwise manner.
- Punctal occlusion- one of the most useful practical approach for conserving tears. Purpose is to decrease physiological outflow of the tear film and enhancing the retention time of tear substitutes.
- Tarsorraphy- it decreases the palpebral height, thus reducing tear evaporation.
Changed
10/Aug/2017
Condition