Dr Pankaj Deshpande, Consultant Pediatric Nephrologist sheds light on common kidney related issues in children - a topic that few people are aware about. In Part 1, he focusses on Kidney stones. And in Part 2, he will talk of urinary bladder issues.
What are the most common nephrologic issues amongst the pediatric population?
The words children and kidney disease seem incongruous to most people. The first reaction on mentioning any kidney illness in babies or children is that they never thought that children could have kidney disease!
That is far from true. Children too have many kidney ailments and the spectrum of diseases is far different from that in adults. Some of the illnesses need early diagnosis and simple management while some may cause problems in adult life. The sad part is that kidney function is not paid the desired attention in children and this can cause long term effects when the child is an adult.
Common ones include urine infections and repeated (recurrent) ones, glomerular diseases like nephrotic syndrome or Nephritis, tubular disorders like Renal Tubular Acidosis, acute kidney failure secondary to various factors that presents as an urgent management problem and finally, chronic kidney disease where the kidneys do not work well and eventually the child/adult would need dialysis and kidney transplantation. The scary part is that not many are even aware that the common cause for this is Renal dysplasia (kidneys not formed normally at birth) and these children would not have any symptoms till a very late stage of kidney failure. Apart from this there are problems like Kidney stones (Urolithiasis) that usually has a cause, wetting problems that may be present in the daytime (during school hours) or bedwetting at night that can affect the child and family in a major way. So, to summarize, the list is long but some of the problems seen in childhood in the kidneys are:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Glomerular diseases like nephrotic syndrome
- Tubular disorders (RTA/Bartters syndrome)
- Acute kidney failure
- Chronic kidney disease (Renal dysplasia)
- Urolithiasis
- Wetting (daytime and/or bedwetting)
Is there a growing incidence of kidney stones in children in India? If yes, what are the causes for this increase?
Kidney stones (Urolithiasis) is again often considered a problem in adults. However even children can get kidney stones. While the general teaching is that kidney stones in children are about 1% of the total incidence in adults, in India we seem to have a far greater prevalence. Babies as young as 6 months of age have been detected to have kidney stones.
In brief, we need to understand the reason for formation of a kidney stone. The urine that each one of us produces is supersaturated with various elements. In simple terms, when this balance is disturbed, the elements can join together and form a nidus (focus) for a stone to form. The important elements here are calcium, oxalate, magnesium and citrate. So, increase in calcium or oxalate in the urine (that are called the stone forming substances) or a decrease in elements like citrate or magnesium (the stone inhibiting substances) will lead to a stone formation. However, the greatest stone inhibiting factor is fluid as that allows the stone forming substances to be away from each other. So, a lack of proper fluid intake is one the biggest factors for stone formation.
In adults, very often no cause for the stone formation can be found. In children, conversely, 75% of the stones have an underlying metabolic cause. If the cause is not identified, children will keep on forming stones repeatedly and not only need treatment over and over again but may also damage the kidneys. There are certain illnesses that are seen only in children that may predispose them to forming stones because the kidneys are formed such that they leak a lot of calcium in the urine throughout life. These include conditions like Renal Tubular Acidosis/Bartters syndrome or Manz syndrome. If not identified, these not only cause stones but also do not allow the child to grow well. Even without any of these illnesses, it is estimated that 5% of the Indian children have hypercalciuria (excreting large amounts of calcium in the urine).
Recently, a change in dietary habits like increased salt intake because of processed/junk food, reduced water intake for multiple reasons and improper attention to a balanced diet has led to an increase in kidney stone formation in children.
Various causes for kidney stones in children are as follows:
- Hypercalciuria (Primary or secondary to condition like RTA etc)
- Hyperoxaluria
- Hypocitraturia
- Low magnesium levels in the urine
- Increased uric acid levels in the urine
- Cystinuria
- Most importantly, a reduced fluid intake
What are the signs and symptoms of nephrolithiasis in children? Is it the same as in adults?
The first important step in kidney stones or urolithiasis is diagnosis of the condition. The common mode of diagnosis is an incidental pick-up when an ultrasound scan of the abdomen is done for any reason. However, we need to take care to note that ‘all that glitters is not gold!’ Hence every scan report that mentions a kidney stone is not necessarily diagnostic or confirmatory of a kidney stone. The size of the stone matters and when the size is less than 5 mm, the probability of a stone being present decreases as is described below.
With regards to the symptoms, we need to understand that as long as the calculus/stone is in the kidney, there are virtually no symptoms. The symptoms occur when the stone starts travelling down the ureters (pipes that lead from the kidneys to the bladder). Hence one may have a fairly large stone sitting in the kidney without any symptom whatsoever.
Sometimes the calcification is within the parenchyma (substance) of the kidney and that is called as nephrocalcinosis. That is not a stone and will not travel down the ureters.
When the stone travels down the ureter, there are severe symptoms. There is often colicky abdominal pain associated with vomiting, blood in the urine (haematuria), flank pain and there maybe dysuria (burning while passing urine). However, one needs to be careful when we attribute symptoms that a child has to a kidney stone. If there is a 2-3 mm calculus sitting within the kidney and the child has red coloured urine (blood in the urine), it is unlikely to be because of that stone (if at all it were a stone in the first place!)
In summary, most stones are likely to be incidental pick-up and will not have any symptoms at all. Hence it is necessary to monitor them to make sure that they have passed. Absence of pain does not mean that there is no kidney stone!
What are the ways to treat or help pass these stones?
The first and foremost thing to ascertain is whether there is a stone present. Just because the ultrasound scan reports a kidney stone does not mean it is present. In this case, ‘size matters!’ The specificity of the ultrasound to diagnose a stone with certainty decreases when the size is below 5 mm. Certain other factors may help to confirm that it is a stone, like shadowing behind the stone or knowing the anatomical position where it occurs. End on view of blood vessels, debris etc can also look like calculi. So, unless confirmed to be a stone, unnecessary tests, expensive imaging and treatment may not be required!
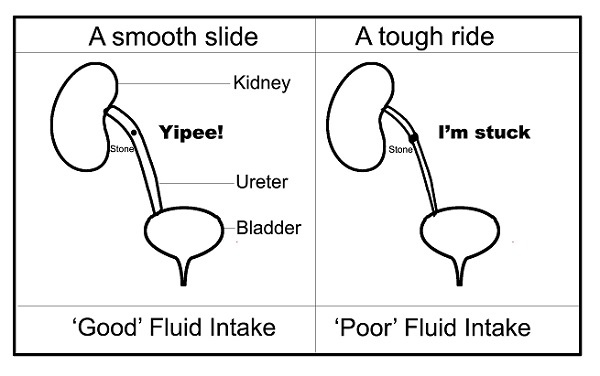
In children, if the size of the calculus is less than 6-7 mm, we can help the stone to pass out naturally. The primary factor in this is increasing fluid intake. When this is mentioned, the child goes from drinking one glass to 2 glasses of water. That is totally pointless and useless! One needs to realise that a 20 kg child normally is required to have about 1.5 litres of fluids daily (hardly any child takes that much fluid!). Now if they have a calculus, that intake should increase to at least 2 litres, if not more. This is the difficult part but without this aspect of treatment all other treatment is pointless. This is not required in a hospital and can be done at home. There is no magic medicine to dissolve the stones (unless they are specific stones like uric acid stones that are quite rare). There are medications that can be used to make the ureter size a bit bigger to allow the stone to pass (calcium channel blockers like Nifedipine or alpha blockers like Tamsulosin). Generally, about 4 weeks is allowed to see if the stone passes out spontaneously.
If the size of the calculus is greater than 8 mm or if it does not pass out spontaneously in 4 weeks, some kind of intervention will be required to remove the stone. That can range from ESWL (Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy) to surgery. During the 4 weeks that we are waiting for the stone to pass out, if there are repeated urine infections, persistent pain not relieved by medications or persistent red urine, intervention may be required.
Finally, and most importantly, unless the root cause of the calculus is addressed, one can be quite sure that it will recur. Hence treatment of the underlying factors causing the stone is as much important as treating the stone itself.
Figure 1: ‘Helping’ the stone ‘pass’!
What measures can parents take to prevent recurrence of stones?
As mentioned above, 75% of kidney stones in children have a metabolic cause that can be identified. Hence the most important aspect is to identify the causative factor.
For this, the stone (if retrieved) has to be sent for analysis. One can ensure retrieval of the stone by asking the child to void urine through a strainer at home. Blood and urine tests to identify the causative factors are an absolute must. Otherwise, recurrence is common.
One of the common reasons for stone formation as explained above is inadequate fluid intake. Hence increasing fluid intake is imperative. A 20 kg child has to drink at least 2 litres of fluid to prevent stone formation. Fizzy, carbonated or salty drinks are not to be used. Most of these children have a low citrate (a stone-inhibiting substance) in the urine. Hence initially, though one may use a citrate supplement the final recourse is to increase citrate content in the diet. This is provided by all kinds of fruits. One of the ironies is that as soon as parents understand about a kidney stone in the child, they stop giving ‘all seed-bearing items’ to the child! As most fruits contain seeds, that becomes the first casualty and children actually reduce the fruit intake, reducing citrate in the urine and causing more stones! A simple logic to be understood is that whatever you eat (seed bearing or not) is in the intestine and cannot go the kidney directly and form a stone! Hence this kind of behaviour based on ‘myths’ should be avoided. All fruits contain citrate in good quantities and citrus fruits like oranges, sweet lime even more so.
One of the other causes is increased calcium in the urine that can be detected on urine tests. One of the typical behaviours is to limit the calcium intake as soon as a stone is diagnosed. That paradoxically will lead to more oxalate in the urine and hence more stone formation! Hence the idea is not to limit calcium completely in the diet but allow the child to have normal calcium in the diet but avoid supplements like Vitamin D or calcium tablets/syrups. If there is excessive calcium in the urine, medications can be used to reduce the calcium in the urine (thiazide diuretics).
It has been shown conclusively that increased salt excretion leads to more calcium in the urine. Hence reducing salt in the diet of the whole family is imperative. Reduction of processed foods/junk foods is essential to reduce the salt intake.
If the work-up (blood and urine tests) indicate any kind of kidney problem (like Renal Tubular Acidosis, Barters syndrome, Manz syndrome, Dent’s disease etc), specialised treatment for that condition will be required to not only make the child better but also to prevent recurrence of stones.
To understand about urinary bladder issues in children, check part 2

Dr Pankaj V Deshpande, MD Pediatrics, MRCP (UK), DCH, FCPS
Consultant Pediatric Nephrologist attached to Hinduja Hospital, Mahim; Apollo hospital, Belapur; Hinduja Health care, Khar; MGM hospital Vashi
MD from Bai Jerbai Wadia hospital/KEM hospital. MRCP, UK with specialization in Pediatric Nephrology. Practiced in Birmingham Childrens Hospital, Guy’s hospital, and Southampton General Hospital, .
Many publications and presentations. Presentations at European Society of Pediatric Nephrology, Pedicon, Embicon, IAP meetings etc.