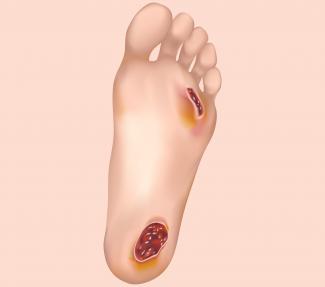
Diabetic foot ulcers occur in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is an open sore or wound that is located on the bottom of the foot. Infection of the wound and other ulcer-related complication can result in hospitalization. Learn to prevent and manage it.
What is diabetic foot ulcer?
Diabetic patients are at a high risk of developing many foot problems. Even simple foot problems can become severe and cause complications. The root cause of most foot complications is nerve damage called diabetic neuropathy. Tingling, burning, pain, loss of sensation or weakness in the foot are all symptoms of neuropathy. Diabetes also causes the blood vessels of the foot and leg to narrow and harden leading to poor blood flow. Poor blood circulation can make healing and fighting infections harder for the foot. Even stepping on a sharp object or stone can become a serious complication. Since ulcers are the most severe of the foot complications seen in diabetic patients, we focus on foot ulcers in this article.
Foot ulcer and its impact
A foot ulcer is where the skin has broken down and the underlying tissue is exposed. Diabetic neuropathy is the biggest factor for loss of feeling in the foot, leading to foot complications, making patients prone to ulcers. Foot ulcers can be caused by friction, trauma and skin lesions. There are various types of ulcers. When a nerve is affected, it is a neuropathic ulcer.
A foot ulcer can begin along a sore, crack, skin tear with symptoms such as swelling, redness, pus, odour and ankle pain.Foot ulcers can take a long time to heal, especially if there are circulation problems.
There is also a higher chance of an ulcer getting infected or, worse, gangrene. Gangrene is death of tissue, which can occur due to infection or loss of blood supply to a part of the body. Immediate medical attention is recommended if you see an ulcer on your foot. A deep ulcer is much harder to treat than a shallow one. Your doctor will assess the ulcer in terms of width and depth and infection, if any. Sometimes infection spreads to nearby bones or joints, which can be difficult to clear, even with a long course of antibiotics. Foot ulcers can lead to limb-threatening or non-limb threatening infections in various parts of the body.
Infection in the ulcer may result in:
- Abscess (big collection of pus)
- Osteomyelitis (infection of the bone)
- Gangrene (deadened area of the limb which becomes black, requiring amputation)
- Ischemic symptoms (symptoms of less blood supply to a particular area)
Are you at risk of diabetic foot ulcer?
You are at a higher risk if you have:
- Untreated or uncontrolled diabetes
- Previous amputation, not necessarily related to diabetes
- Previous ulcers on the foot
- Any deformities of the foot
- Male with history of peripheral vascular disease
Can diabetic foot ulcer be prevented?
Take the following precautions:
- It is very important to maintain blood sugar at the prescribed level and have regular vascular evaluations (non-invasive check-up of the arteries and veins)
- Inspect your feet regularly for dry skin, calluses, ulcers, blisters or other injuries – this is crucial in avoiding complications and treating the foot problem early
- Keep feet clean and moisturise daily to prevent cracks and dryness
- Avoid keeping feet wet and check for fungal infections like Athlete’s foot, especially between the toes
- Cut toe nails often to prevent ingrowth, infection or injury
- Never walk barefoot. Always wear socks or footwear even at home. However do not wear socks that are too tight that may constrict blood flow.
- Wear comfortable, fitting shoes, preferably close-toed to prevent injury to toes
- All foot problems must be looked at by a medical professional. Do not try to treat corns, calluses, verrucas or other foot problems by yourself.
- Eat a healthy diet (sugar- and salt-free) and exercise daily
- Control blood pressure (below 130/80 Hg). This will help reduce damage to blood vessels and circulation.
- Quit smoking to help reduce vascular (heart) problems.
Stages of ulcer and treatment
1. Low risk normal foot
- A normal foot without any ulcer
- No deformities
- No history of ulcer or amputation
Treatment
- Preventive care, keeping the foot clean and avoiding infection
- Education and reference for risk reduction, eg diabetes management, smoking cessation and other behavioural changes like stress management
2. High risk abnormal foot
- An abnormal foot without any active ulcer
- Deformities (amputated area)
- History of ulcer and amputation
Treatment
- Patient education
- Protective footwear
3. High risk simple ulcer
- An active ulcer with superficial skin involvement
- Ulcer <2 cm wide without infection or systemic manifestations (kidney, heart etc) and intact vascular status i.e. it has not affected any other organs
Treatment
- Outpatient wound care until the ulcer heals
- Frequent follow-up
- Patient education
- Protective footwear
- Appropriate referrals to foot care specialists, rehabilitation and orthopedics are important for management
4. High risk complex ulcer
- An active ulcer that covers an extensive area
- Ulcer >=2 cm wide infection
- Hyperglycaemia
- Vascular disease
- Symptoms present in various systems of the body i.e. the infection has spread to other organs.
Treatment
- Inpatient wound care
- Revascularisation due to blockage in the vessels. Other vessels going alongside the affected vessel compensate the function of supplying blood. If the primary vessel is not very damaged, it regains its functionality with medication and proper nutrition.
- Minor amputation, if required.
Additionally, in stages 3 and 4, the doctor may take the following steps:
- Wide surgical debridement (ie removal of tissue with surgery)
- Tissue culture for infections (to check for the presence of particular bacteria)
- Sterile dressing changes with Becaplermin gel
- No weight-bearing is recommended for neuropathic ulcers with adequate blood supply. Putting body weight on the foot with the ulcer can lead to more problems. Patients have to keep off their feet for speedy recovery.
- Prescribing oral or parenteral (intravenous) antibiotics to control Staphylococcus and Streptococcus (micro-organisms that are common sources of infection) in deep space (ie, infections are no longer in superficial layer of skin). Intravenous antibiotics act faster since they enter the blood stream directly, so they are preferred over oral antibiotics, which take longer to act.
- Regular follow-up is needed with education on foot care
The treatment is considered to be successful when these targets are achieved:
- HbA1c <7% for prevention
- Complete healing of ulcer
- Prevention of recurrence
Regular monitoring by self and provider is needed.