The function of the kidney is to rid the body of toxins and to purify the blood. Diabetes can reduce the kidney’s ability to filter waste products, leading to build-up of waste products in the body.
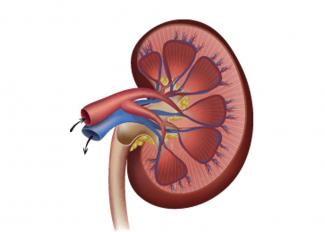
Anatomy of the kidney
This is how the kidney works: The end functioning unit of the kidney is the glomerulus, which filters out ammonia, urea and other chemicals from the blood entering the kidneys. Blood vessels that enter the kidney are called afferent and those exiting are called efferent. The afferent brings in the impure blood, which drains into pouch-like structure called the glomerulus where ammonia, urea etc is filtered out. The blood that is free of impurities exits through efferent blood vessels.
The glomerulus’ power of filtration is called the Glomerulus Filtration Rate (GFR), a reading that indicates whether the blood is being filtered properly or not. If the glomerulus filters well, the blood is free of impurities. The optimal filtration rate should be between 90-120 ml/min/1.73m2 for at least 3 months. Any variation should be investigated.
Diabetic nephropathy and its impact
Diabetes makes the kidneys filter too much blood, thus overworking them. Over time, the filtration system becomes inefficient. Waste products build up in the blood and the kidney leaks small amounts of protein into the urine. The presence of protein in urine is termed microalbuminuria, which is a bad sign. Without proper treatment to slow down the progression of the disease, the kidneys will fail and the patient may need to undergo kidney transplant.
Approximately 20-30 per cent of Types 1 and 2 diabetics develop nephropathy or diseased kidney. The most common form is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), which is defined as the kidneys having Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) of < 60ml/min/1.73m2 for 3 or more months.
Are you at risk
Increased blood sugar predisposes all diabetics to complications, including kidney damage.
Can nephropathy be prevented
Keeping blood sugar levels under control is the best preventive measure. Avoid smoking and drinking excessive amounts of alcohol. Regular exercise and a healthy, balanced diet is recommended. It is advisable to check kidney function every year.
Symptoms
Most people with CKD have few or no symptoms. Some of the symptoms to look out for are:
• Swollen ankles, feet or hands (due to water retention)
• Shortness of breath
• Decrease in appetite and weight loss
• Itchy skin
• Nausea
• Blood or protein in your urine (protein is detected on a urine test)
• Increased urination (particularly at night)
• Muscle cramps
• High blood pressure (hypertension)
• Erectile dysfunction in men (an inability to get or maintain an erection)
What kind of screening tests should I have done
According to the International Diabetes Center, Type 1 diabetics should be screened at least 5 years after diagnosis of diabetes and annually thereafter. Type 2 diabetics should be screened on diagnosis and annually thereafter. Risk factors should be assessed and a testing of albumin to creatinine ratio - A/C ratio – is to be repeated annually. (A/C ratio of the first morning urine sample should be done at least on three consecutive days. If two of the readings show >30 mg/gm/24 hours, it signifies a diseased kidney.)
Stages of nephropathy
Here are the five stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) that are mainly based on measured or estimated Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measured in ml/min/1.73m2. All GFR values are normalised to an average surface area (size) of 1.73m2
Stage 1: Renal Hypertrophy and glomerular hyperfiltration
Kidney damage* with normal or increased GFR >=90
Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of the kidney. Hyperfiltration is increased filtration due to increase in size of glomeruli or increased blood flow. This occurs with uncontrolled blood sugar and returns to normal with good blood sugar control.
Stage 2: Apparent normalcy
Kidney damage* with mildly decreased GFR 60-89
This stage is clinically silent, which means that there are no clinical or laboratory signs of the disease. Symptoms such as urinary tract infections may show up after 5 to 15 years of a patient being diagnosed as a diabetic. Such symptoms can persist even when managed, hence frequent check-ups are required. In case of blood sugar of less than 250 mg/dl, there will be a reduction of GFR although not regularly seen at this stage.
Stage 3: Microalbuminuria or incipient nephropathy
Moderately decreased GFR 30-59
This refers to an increase in albumin in the urine. This may occur in 20-30 per cent of diabetics after they have had the disease for 6-15 years. The ideal protein (albumin) in the urine is 30-300 mg/24 hours.
Stage 4: Overt (or established) nephropathy
Severely decreased GFR 15-29
This is the classic stage showing kidney damage with its major characteristic being a persistent proteinuria, i.e. protein found in urine. If the amount of protein is more than 0.5grams per 24 hours, it indicates significant protein loss.
Stage 5: End-stage renal disease
Kidney failure; GFR < 15 or dialysis
Found in 25% of diabetic patients, both insulin-dependent and non insulin-dependent. Uremia (elevated blood urea nitrogen level) due to diabetes mellitus is the major problem seen in this stage.
*Kidney damage is defined as abnormalities on pathological, urine, blood or imaging tests.
Treatment
As per the latest American Diabetes Association 2013 Guidelines, here are some of the options:
• If you are not pregnant, patients with modestly elevated (30-299 mg/day) or higher levels (>300 mg/day) of urinary albumin excretion, may be prescribed drugs like ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitors or ARBs (angiotensin receptor blockers).
• Those with diabetes and the early stages of CKD are recommended reduced protein intake of 0.8–1.0 g/kg of body weight per day. Those in the later stages of CKD are advised to take 0.8g protein/kg of body weight per day. This may improve measures of renal function (urine albumin excretion rate, GFR).
• When taking drugs such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs or diuretics, monitor serum creatinine and potassium levels for the development of increased creatinine or changes in potassium.
• Reduce the dietary intake of salt to 5g per day to slow the progression of renal disease.
• Continued monitoring of urine albumin excretion to assess both response to therapy and progression of the disease.
• When GFR is 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or less, evaluate and manage potential complications of Chronic Kidney Disease.
• Consider referral to a physician experienced in the care of kidney disease for uncertainty about the etiology of kidney disease, difficult management issues or advanced kidney disease.
Read more on Chronic Kidney Disease : http://www.patientsengage.com/condition/chronic-kidney-disease