Cervical cancer refers to cancer that originates in the cells lining the cervix, which is the organ connecting the uterus and the vagina.
There are two main types of cervical cancers: The most common is squamous cell carcinoma, arising in the squamous (flattened) epithelial cells that line the cervix. The other is adenocarcinoma, which starts in the mucus-producing gland cells of the cervix. The human papilloma virus (HPV) infection is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
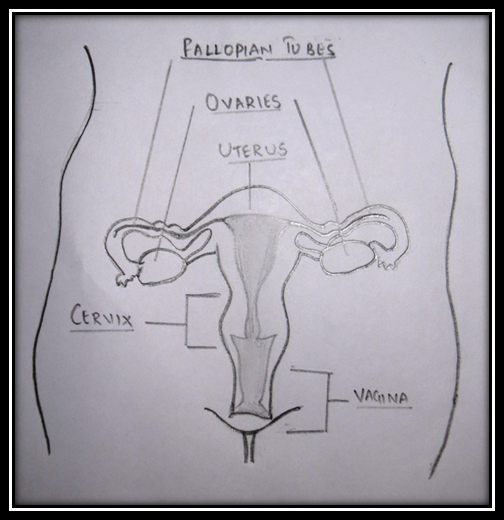
Anatomy of the cervix
The cervix (Latin: neck) is a part of the female reproductive system that lies between the uterus and the vagina. The cervix has a central canal with an internal and external opening, and is between two and three centimeters long. The ectocervix refers to the part of the cervix that links to the vagina, and the endocervix is the part of the cervix that opens into the uterus.
The cervix is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilise an egg after sexual intercourse. It is also important in fertility, contraception and childbirth. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms aim to block the cervix. During vaginal childbirth, the cervix must flatten and dilate to allow movement of the fetus.
The cervix has an epithelium (tissue layer) and as women age, the epithelial cells change their shape, going from column-like cells to multiple layers of flat cells. Because of this change, known as metaplasia, the epithelium of the cervix is at increased risk of cancer.