A stroke is caused by the interruption of the blood supply to the brain, usually because a blood vessel bursts or is blocked by a clot. This cuts off the supply of oxygen and nutrients, causing damage to the brain tissue.
The effects of a stroke depend on which part of the brain is injured and how severely it is affected. A very severe stroke can cause sudden death.

Here are some of the general symptoms noticed in a stroke:
- Sudden-onset face weakness
- Arm drift (ie, if a person, when asked to raise both arms, involuntarily lets one arm drift downwards)
- Abnormal speech
Some symptoms depend upon the part of brain involved. If the brain stem (the part that joins the brain to the spine) is affected, it may result in the following: Altered smell, taste, hearing or vision (total or partial)
- Drooping of eyelid and weakness of eye muscles
- Decreased sensation and muscle weakness of the face
- Balance problems
- Altered breathing and heart rate
- Weakness in neck muscle with inability to turn head to one side
- Weakness in tongue (inability to move tongue from side to side)
If the middle part of the brain is involved, it can produce the following symptoms:
- Difficulty with speaking, hearing, reading and/or writing
- Speech disorder resulting from nerve injury
- Loss of vision
- Memory deficits
- Disorganised thinking, confusion
If the little brain (the part located at the back of the brain) is involved, the patient may have the following:
- Altered walking gait
- Altered movement coordination
- Improper balance
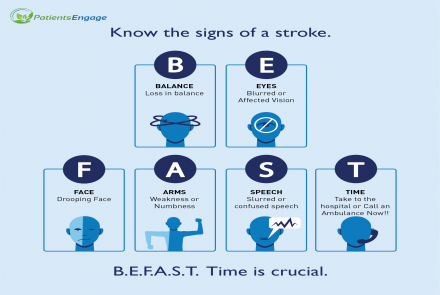
As you can see the symptoms of stroke are complex. Understand the importance of acting quickly and following FAST
FAST - Face, Arm, Speech, Time
- Is the Face uneven
- Is the Arm hanging down or Leg not working as expected
- Is the Speech slurred
- Time - rush to a hospital quickly - within 4.5 hours
Changed
24/Oct/2021
Condition