Stroke or Cardiovascular accident or CVA is a real medical emergency. Quick and timely intervention helps. Dr. Shital Raval tells what you should do to help someone having a stroke.
Stroke, also called Cardiovascular accident or CVA, is a Medical emergency! It occurs when blood flow to the brain or part of the brain become restricted or blocked. This may lead to damage or death of the brain cells from lack of oxygen causing temporary or permanent impairment of the functioning of the brain and affected areas.
How to recognize stroke?
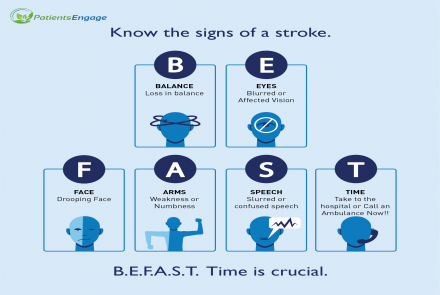
Depending on the severity of the stroke, symptoms may vary. However, the standard way is to check is by using the FAST method:
Face numbness or drooping on one side. Ask patient to smile to check.
Arm numbness or weakness. Ask patient to raise both arms and bring them down.
Speech slurring or garbling. Ask patient to tell you her name to enable talk.
Time is of essence! If the above 3 symptoms are present, call emergency/ambulance services right away.
A person may also be having any of these other stroke symptoms:
- Headache
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the body
- Dim or blurry vision especially in one eye
- Nausea
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
What can you do to help after you call for help?
- Put the patient in safe, comfortable position. Make sure he/she is lying on one side with their head, chin and shoulders slightly elevated.
- Loosen any tight clothing around the neck (tie, scarf, etc.) to ensure the person can breathe better.
- Stay calm and reassure the patient that help is near.
- Check to see if the patient is breathing. If they are not breathing, perform CPR*.
- Avoid moving the person.
- Do not allow the person to eat or drink anything.
Act Immediately to Help Someone having a Stroke
If you suspect that you or someone else is having stroke, act on it immediately. Even if symptoms are mild or subtle, call for emergency services to have it checked out. Brain cells can start to die within minutes. There is only a 3 to 4 hour window within which clot-breaking drugs (thrombolytics) can be useful to restore the blood flow to the brain. This can significantly reduce risk of permanent damage or disability.
*If you don’t know CPR, please do not attempt it, wait for medical help.